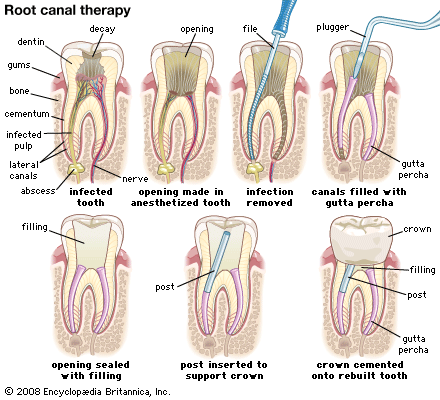
As a rule of thumb, if you have a root canal performed on a tooth, you should expect to have a crown placed afterwards. Crowns help restore the structure and rigidity to a tooth after it has been "hollowed out" by the root canal process. In a few instances, a dentist may not recommend placing a crown on a tooth as part of definitive treatment. However, these cases are certainly the exception, and not the rule.
To perform a root canal, an opening has to be created to access the nerve space within the tooth. This involves removing important structural components of the dental enamel, and thus rendering the tooth much more likely to fracture. A crown remedies this problem by creating a solid cap around the tooth that braces it against biting and chewing forces. Root canal treated teeth also frequently require buildups to replace lost tooth structure and posts to resist against lateral and shearing forces. The cost and time investment of these treatments need to be considered when you choose to have a root canal performed. Without them, the tooth has an much higher chance of breaking during normal use.
In some cases, a dentist will not recommend placing a crown on a root canal treated tooth. Depending on how the patient bites and how much natural tooth structure remains, anterior (front) teeth do not always need crowns. Because they are not primary chewing teeth, the front teeth tend to deal with much less force than the canines, premolars or molars. Additionally, teeth opposing (biting into) dentures or teeth that have nothing to chew against may not need crowns after root canal treatment. In these instances, there is not enough force generated to put the weakened tooth at risk.
In general, expect to need a crown placed as part of completing your root canal treatment. At Thousand Oaks Family Dentistry, we do our best to inform patients of their complete treatment needs- from start to finish. If you would like to learn more about root canals, crowns, fillings or cavities, please give our office a call!